Consuming FXRMotionControllerData in C++
important
Unreal Engine versions 5.2, 5.3, and 5.4 are limited to
FXRMotionControllerData since at the time of their release no
FXRHandTrackingState was available.
Also please keep in mind that, while FXRMotionControllerData is pretty much
usable and functional in Unreal Engine 5.5, it is recommended to utilize
FXRHandTrackingState instead. This is because this version of UE has
deprecated FXRMotionControllerData in favor of the
FXRMotionControllerState and FXRHandTrackingState structs. Prior to
version 5.5, FXRMotionControllerData handled both motion controller and
hand tracking data. From 5.5 onward, these responsibilities have been
separated into the two distinct structs, providing clearer and more
specialized handling of each.
Before continuing this section, please ensure you've first studied the Consuming FXRMotionControllerData section.
Drawing and Animating Virtual Hands
-
Create a new Virtual Reality project based the Unreal VR Template.
-
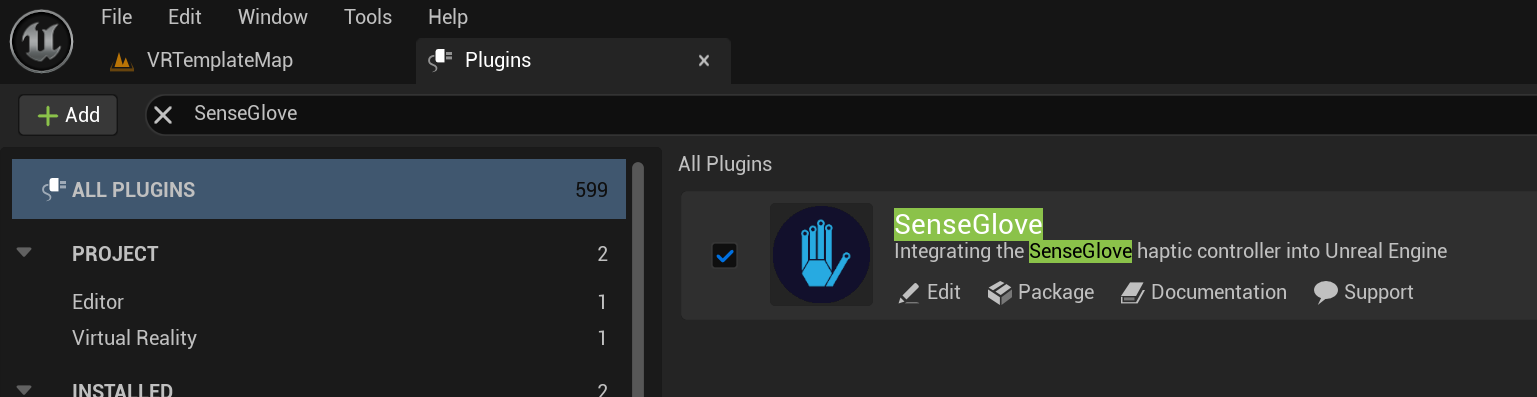
Make sure the SenseGlove UnrealEngine plugin is installed and enabled inside your new project.
-
You could use either hand-tracking or a SenseGlove device as the input data, or both of the inside the same project. Whether you would like to use hand-tracking or a SenseGlove device, please make sure the required steps are taken for each of those first.
-
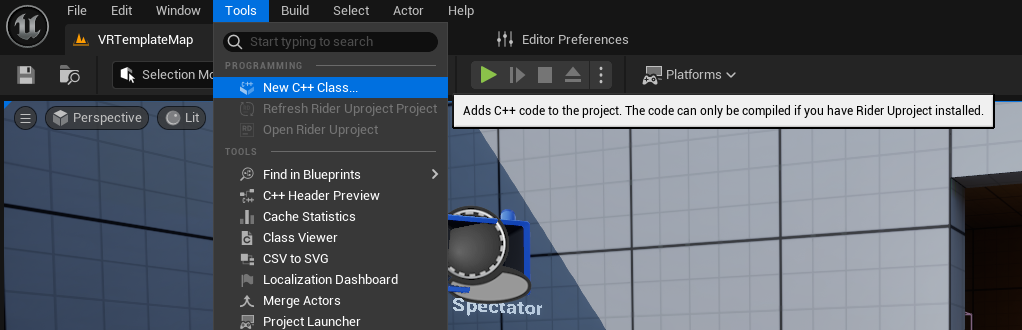
From the
Toolsmenu chooseNew C++ class....
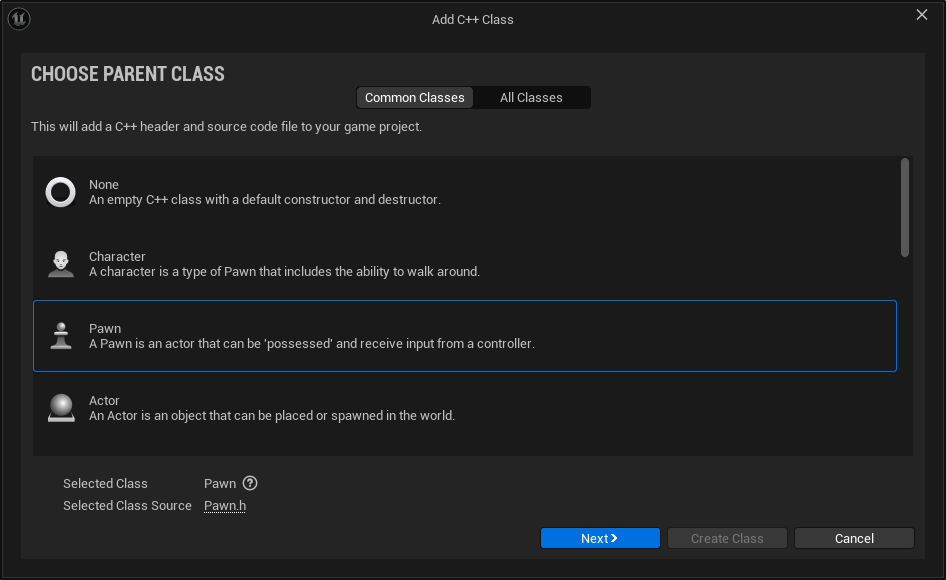
- Choose the Unreal Engine's
APawnclass as the parent class for the new C++ pawn class.
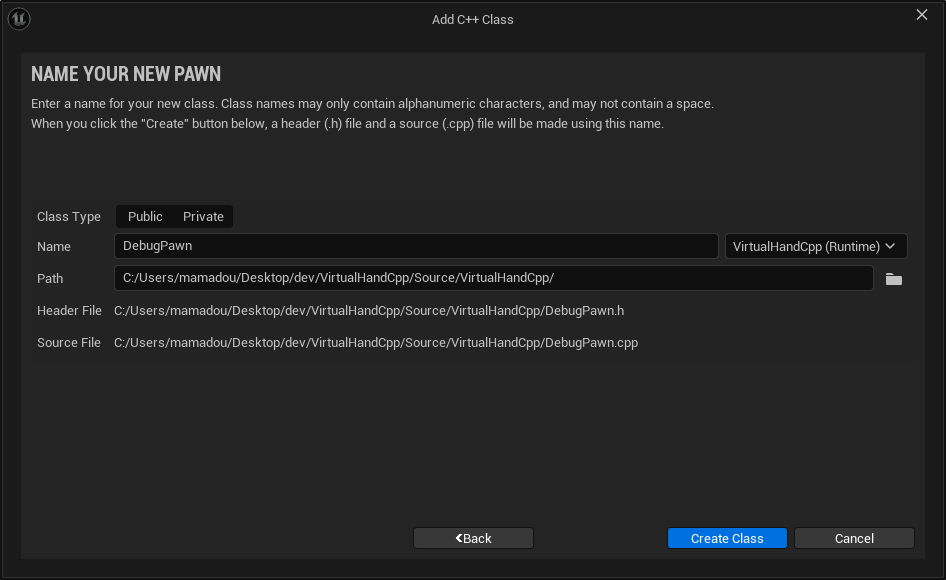
- Name the new pawn class
DebugPawn.
-
Since we have created a new C++ class, this converts the current Blueprint VRTemplateMap project to a C++ one. That's why the Unreal Editor will give us a few prompts regarding opening the project in the default IDE and rebuilding the code. It might be simpler to just close the editor, then rebuild the source code inside your favorite IDE, and then start the editor with the converted project again.
-
Find and open the VRPawn Blueprint Class located at
/Content/VRTemplate/Blueprints/VRPawninside the Blueprint Editor and from theFilemenu choose theReparent Blueprintclass.
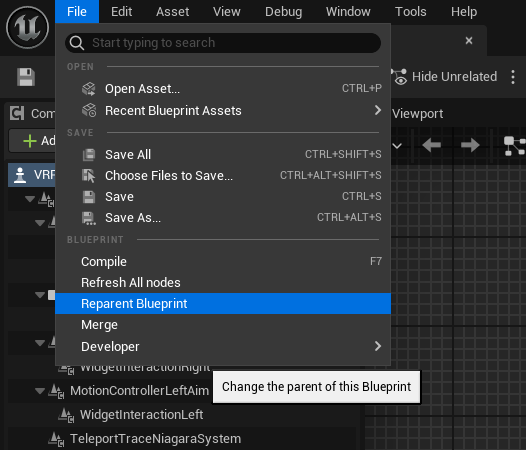
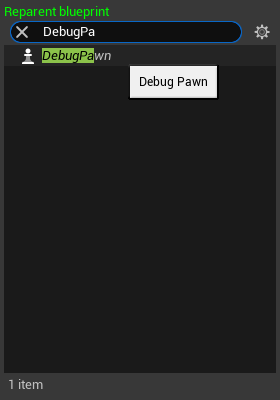
- In the new
Reparent blueprintwindow chooseDebugPawnas the new parent.
- By looking at the
Parent Classlabel located under the Blueprint Editor window control buttons verify that theADebugPawnclass has been set as the new parent.
- Locate the project's main Build file, in our case
VirtualHandCpp/Source/VirtualHandCpp/VirtualHandCpp.Build.csand add theInputDevice,OpenXRHMD,SenseGloveBuildHacks,SenseGloveDebug,SenseGloveSettings, andSenseGloveTrackingmodules as either a private or public dependency.
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
using UnrealBuildTool;
public class VirtualHandCpp : ModuleRules
{
public VirtualHandCpp(ReadOnlyTargetRules Target) : base(Target)
{
PCHUsage = PCHUsageMode.UseExplicitOrSharedPCHs;
PublicDependencyModuleNames.AddRange(new string[] { "Core", "CoreUObject", "Engine", "InputCore" });
PrivateDependencyModuleNames.AddRange(new string[]
{
"InputDevice",
"OpenXRHMD",
"SenseGloveBuildHacks",
"SenseGloveDebug",
"SenseGloveSettings",
"SenseGloveTracking"
});
// Uncomment if you are using Slate UI
// PrivateDependencyModuleNames.AddRange(new string[] { "Slate", "SlateCore" });
// Uncomment if you are using online features
// PrivateDependencyModuleNames.Add("OnlineSubsystem");
// To include OnlineSubsystemSteam, add it to the plugins section in your uproject file with the Enabled attribute set to true
}
}
-
Locate the C++ header and source file for the
ADebugPawninside the project in your C++ IDE. In our case they are located atVirtualHandCpp/Source/VirtualHandCpp/DebugPawn.handVirtualHandCpp/Source/VirtualHandCpp/DebugPawn.cpp. -
Modify the
DebugPawn.hheader file to look like this:
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/Pawn.h"
#include "SGSettings/SGDebugGizmoSettings.h"
#include "DebugPawn.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class VIRTUALHANDCPP_API ADebugPawn : public APawn
{
GENERATED_BODY()
private:
// The virtual hand drawing settings.
UPROPERTY(EditDefaultsOnly, Category="DebugPawn",
meta=(AllowPrivateAccess="false"))
FSGDebugGizmoSettings HandDrawingSettings;
public:
// Sets default values for this pawn's properties
ADebugPawn();
protected:
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
public:
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override;
// Called to bind functionality to input
virtual void SetupPlayerInputComponent(class UInputComponent* PlayerInputComponent) override;
private:
// The method responsible for drawing a virtual hand.
void DrawHand(EControllerHand Hand) const;
};
- Modify the
DebugPawn.cppimplementation file to look like this:
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
#include "DebugPawn.h"
#include "SGDebug/SGDebugGizmo.h"
#include "SGTracking/SGXRTracker.h"
// Sets default values
ADebugPawn::ADebugPawn()
{
// Set this pawn to call Tick() every frame. You can turn this off to improve performance if you don't need it.
PrimaryActorTick.bCanEverTick = true;
// Set the default virtual hand drawing settings.
HandDrawingSettings = FSGDebugGizmoSettings{
1.0f,
FColor{255, 0, 0, 255},
FColor{0, 255, 0, 255},
FColor{0, 0, 255, 255},
false,
1.1f,
0,
0.2f,
};
}
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
void ADebugPawn::BeginPlay()
{
Super::BeginPlay();
}
// Called every frame
void ADebugPawn::Tick(float DeltaTime)
{
Super::Tick(DeltaTime);
// Attempt at drawing the left/right virtual hands every frame.
DrawHand(EControllerHand::Left);
DrawHand(EControllerHand::Right);
}
// Called to bind functionality to input
void ADebugPawn::SetupPlayerInputComponent(UInputComponent* PlayerInputComponent)
{
Super::SetupPlayerInputComponent(PlayerInputComponent);
}
void ADebugPawn::DrawHand(const EControllerHand Hand) const
{
// Get the world and cache it, if it's null we return early.
UWorld* World{GetWorld()};
if (!IsValid(World))
{
return;
}
FXRMotionControllerData MotionControllerData;
const bool bGotMotionControllerData = FSGXRTracker::GetMotionControllerData(
World, Hand, MotionControllerData);
// Return if the struct data is invalid!
if (!bGotMotionControllerData || !MotionControllerData.bValid)
{
return;
}
// Return if the device is not being tracked!
if (MotionControllerData.TrackingStatus == ETrackingStatus::NotTracked)
{
return;
}
// Ensure that MotionControllerData.DeviceVisualType is a hand!
if (!ensureAlwaysMsgf(MotionControllerData.DeviceVisualType
== EXRVisualType::Hand,
TEXT("Invalid DeviceVisualType type!")))
{
}
// Ensure that MotionControllerData.HandKeyPositions has the position data
// for 26 joints!
if (!ensureAlwaysMsgf(MotionControllerData.HandKeyPositions.Num()
== EHandKeypointCount,
TEXT("Invalid HandKeyPositions count!")))
{
return;
}
// Ensure that MotionControllerData.HandKeyRotations has the rotation data
// for 26 joints!
if (!ensureAlwaysMsgf(MotionControllerData.HandKeyRotations.Num()
== EHandKeypointCount,
TEXT("Invalid HandKeyRotations count!")))
{
return;
}
// Iterate over the hand joint positions and rotations!
for (int32 JointIndex = 0; JointIndex < EHandKeypointCount; ++JointIndex)
{
const FVector& JointPosition{
MotionControllerData.HandKeyPositions[JointIndex]
};
const FQuat& JointRotation{
MotionControllerData.HandKeyRotations[JointIndex]
};
// Draw a single joint's gizmo!
// Please note that we could alternatively:
// Use FSGDebugCube::Draw() to draw a cube.
// Or use the FSGDebugVirtualHand::Draw() method and pass the
// MotionControllerData directly to draw the virtual hand
// all at once without iterating the joints. But, that's not
// goal of this tutorial.
FSGDebugGizmo::Draw(World, JointPosition, JointRotation, HandDrawingSettings);
}
}
- Now, rebuild the source code and go back to the
VRTemplateMap, then use the VR Preview button to run the game. If everything's done correctly, you should be able to see the virtual hands inside your VR simulation.
![]()